OpenRailwayMap/Tagging in France
Signalling
All railway signals have the following tags:
- ref=*: unique signal identifier
- railway=signal
- railway:signal:direction=(forward/backward/both) according to the direction of the way.
- railway:signal:position=(left/right/bridge/overhead/in_track)
- railway:position:exact=365.913 where 365.913 is an example. Position of the signal according to the direction of the way. This is the Kilometric point (PK) of the signal installation relative to the start of the line.
Main Signals
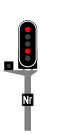
Carré
An absolute stop signal for normal train operations, typically found on main lines or at stations. The signal displays two steady red lights, arranged either vertically or horizontally. It is equipped with a clearing light (referred to as an œilleton in French), which is illuminated in all states except when the signal is closed (i.e., displaying the FR:C state). The signal also features an identification plate bearing the inscription Nf in white letters on a black background.
The signal may also be equipped with a marker plate (railway:signal:main:caption:marker tag) and/or a block plate (railway:signal:main:plate:block and railway:signal:main:caption:block tags) indicating the block system downstream of the signal. The inscriptions on these plates are written in black letters on a white background.
- railway:signal:main=FR:CARRE
- railway:signal:main:height=(dwarf/normal) (optional; default is normal)
- railway:signal:main:clearing_light=(yes/no) (optional; default is yes)
- railway:signal:main:caption:block=* (optional; text written on the block plate)
- railway:signal:main:caption:marker=* (optional; text written on the marker plate)
- railway:signal:main:plate:block=(FR:BM/FR:PR) (optional; block plate)
- railway:signal:main:plate:departure=(yes/no/request) (optional; default is no. Set to yes if the signal is equipped with a half-white, half-green plate, or request if it is equipped with a Demande de Départ plate)
- railway:signal:main:short_route=(yes/no) (optional; default is no. Set to yes if the signal is topped with a luminous yellow stripe)
- railway:signal:main:form=light
- railway:signal:main:shape=(FR:C/FR:F/FR:H) (optional and only if railway:signal:main:height=normal).
- railway:signal:main:states=* (→ available states, separated by
;)
In some stations, the entrance Carré signal may be topped with a luminous yellow stripe (Bande jaune). This stripe is lit in addition to the announcement (Avertissement) signal. It instructs the driver to be prepared to stop at the platform within a short distance, either due to the presence of vehicles or the closure of an intermediate stop signal.
Carré violet
An absolute stop signal, similar to the Carré signal, specifically used to control train movements during shunting operations, on service tracks, or during transitions of traffic to and from main lines. The signal displays a single steady purple light and is also equipped with an identification plate bearing the inscription Nf in white letters on a black background.
Like the Carré signal, this signal may be equipped with a marker plate and/or a block plate with inscriptions in black letters on a white background.
- railway:signal:main=FR:CV
- railway:signal:main:caption:marker=* (optional; text written on the marker plate)
- railway:signal:main:plate:block=(FR:BM/FR:PR) (optional; block plate)
- railway:signal:main:caption:block=* (optional; text written on the block plate)
- railway:signal:main:form=light
- railway:signal:main:height=(high/low)
- railway:signal:main:shape=(FR:A/FR:C/FR:F/FR:H) (optional)
- railway:signal:main:states=* (→ available states, separated by
;)
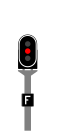
Sémaphore
A stop signal that can be passed under certain conditions. The signal may display either a steady or flashing red light. It is also equipped with an Identification Plate featuring one of the following inscriptions in white letters on a black background:
- F (for Franchissable, indicating a block of Block Automatique Lumineux)
- BM (indicating a block of Block Manuel)
- PR (indicating a block of Block Automatique à Permissivité Restreinte)
The actual inscription is specified with the railway:signal:main:plate tag.
- railway:signal:main=FR:S
- railway:signal:main:caption:marker=* (optional; text written on the marker plate)
- railway:signal:main:plate=(FR:F/FR:PR/FR:BM) (identification plate)
- railway:signal:main:form=light
- railway:signal:main:shape=(FR:A/FR:F) (optional)
- railway:signal:main:states=* (→ available states, separated by
;)
Guidon d'Arrêt
A stop signal that requires the driver to come to a complete stop before the signal. When in the open position, the signal does not display any specific indication other than the red stripe being extinguished. It is equipped with an identification plate with the inscription GA and may also have a marker plate, both featuring inscriptions in black letters on a white background.
- railway:signal:main=FR:GA
- railway:signal:main:form=light
- railway:signal:main:caption:marker=* (optional; text written on the marker plate)
Distant Signals
Disque
A Disque (Disk) signal instructs the driver to proceed at sight (Marche à Vue) as soon as possible or to stop before the first set of points (switch or crossing) protected by the disk. It is equipped with an identification plate bearing the inscription D in black letters on a white background.
- railway:signal:distant=FR:D
- railway:signal:distant:caption:marker=* (optional; text written on the marker plate)
- railway:signal:distant:form=light
- railway:signal:distant:states=* (→ available states, separated by
;)
Avertissement
An Avertissement (Announcement) signal indicates the approach to a closed sémaphore of Block Automatique à Permissivité Restreinte (BAPR). It is equipped with an identification plate bearing the inscription A in black letters on a white background.
- railway:signal:distant=FR:A
- railway:signal:distant:caption:marker=* (optional; text written on the marker plate)
- railway:signal:distant:form=light
- railway:signal:distant:states=* (→ available states, separated by
;)
Disabled Signal
Use
Speed Limits
Speed limits are signaled by Speed Indicators called Tableau Indicateur de Vitesse limite (TIV); TIVs can be either mobile, fixed or pentagonal.
Mobile Speed Indicators
Switches that can only be crossed at reduced speed in the thrown direction (approximately 60 km/h) are typically preceded by two mobile TIVs: a diamond-shaped TIV à Distance (TIV-D) followed by a speed limit reminder called TIV de Rappel (TIV-R).
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant=FR:TIV-D
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:form=sign/light
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:states=closed
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:speed=100
- railway:crocodile=yes (if equipped with crocodile)
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant=FR:TIV-D
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:form=light
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:states=open
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:speed=none
- railway:crocodile=yes (if equipped with crocodile)
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant=FR:TIV-D
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:form=light
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:states=closed
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:speed=100
- railway:crocodile=yes (if equipped with crocodile)
The TIV-R is always paired with the Carré signal preceding the point.
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder=FR:TIV-R
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder:states=closed
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder:speed=60
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder=FR:TIV-R
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder:states=closed
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder:speed=80
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder=FR:TIV-R
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder:form=light
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder:states=open
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder:speed=none
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder=FR:TIV-R
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder:form=light
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder:states=closed
- railway:signal:speed_limit_reminder:speed=60
Chevron
Additionally, if necessary, the location of the point (or the first point in the case of successive points) is identified by a downward-pointing Chevron.
- railway:signal:speed_limit=FR:CHEVRON_BAS
- railway:signal:speed_limit:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit:type=downwards (optional; downwards by default)
Fixed Speed Indicators
Fixed Distant Speed Indicators (Ordinary Type)
Fixed distant speed indicators of ordinary type (TIV fixes à distance du type ordinaire) are usually square in shape. They are diamond-shaped when the speed limit is less than or equal to 40 km/h.
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant=FR:TIV-D
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:form=(light/sign)
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:speed=80
- railway:crocodile=yes (if equipped with crocodile)
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant=FR:TIV-D
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:form=(light/sign)
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:speed=40
- railway:crocodile=yes (if equipped with crocodile)
The Z sign is the execution signal indicating the start of the zone to be traveled at limited speed.
- railway:signal:speed_limit=FR:Z
- railway:signal:speed_limit:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit:function=entry
The R sign indicates the end of the zone where the speed limit is required and the return to normal speed (Reprise de vitesse).
- railway:signal:speed_limit=FR:R
- railway:signal:speed_limit:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit:function=exit
- railway:signal:speed_limit:speed=none
Fixed Distant Speed Indicators (Type B)
Fixed distant speed indicators (TIV-D) of type B indicate that the speed limit must be observed by trains authorized to travel at speeds greater than 140 km/h. When only TIV-D of type B signals are present, the speed limit also applies to self-propelled trains (automoteurs).
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant=FR:TIV-D
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:type=FR:B
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:speed=*
Fixed Distant Speed Indicators (Type C)
Fixed distant speed indicators (TIV-D) of type C specifically apply to railcars and self-propelled trains (autorails et automoteurs).
When a TIV-D of type B is paired with a TIV-D of type C, the speed limit shown by the TIV-D of type B applies only to trains authorized to exceed 140 km/h. The TIV-D of type C serves as a reminder of the upstream speed limit for railcars and self-propelled trains.
If the speed limit differs between pendular trains and other self-propelled trains, the TIV-D of type C displays two numbers. The lower section with the higher number, in italics, indicates the speed limit for pendular trains, while the upper section shows the speed limit for other self-propelled trains.
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant=FR:TIV-D
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:type=FR:C
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:speed=* (separated by
;if more than one speed limit has to be specified)
Speed Limit Announcement (P board)
The P board announces a distant speed indicator (TIV-D) for lines equipped with pre-announcement signalling. This sign applies only to trains running at speeds higher than 160 km/h and requires the train to pass the next TIV-D at a speed lower than 160 km/h. This sign is lit at night.
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant=FR:P
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:speed=*
Pentagonal Speed Indicators
Pentagonal TIVs typically concern freight trains and possibly certain locomotive series. The TIV figure specifies the maximum speed in tens of kilometers per hour (e.g. 5 stands for 50 km/h).
A distant upward-pointing pentagonal speed indicator (TIV-D) announces a special speed restriction. When the restriction applies only to certain locomotive series, the pentagonal TIV-D is accompanied by an L plate placed below it.
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant=FR:TIV_PENDIS
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:plate=FR:L (optional)
- railway:signal:speed_limit_distant:speed=*
A downward-pointing pentagonal TIV, with a white digit on a black background, serves as the execution signal indicating the beginning of the track section to be traversed at a limited speed.
- railway:signal:speed_limit=FR:TIV_PENEXE
- railway:signal:speed_limit:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit:function=entry
- railway:signal:speed_limit:speed=*
A downward-pointing pentagonal TIV without any markings indicates the end of the track section to be traversed at a limited speed.
- railway:signal:speed_limit=FR:TIV_PENREP
- railway:signal:speed_limit:form=sign
- railway:signal:speed_limit:function=exit
- railway:signal:speed_limit:speed=none
Repère de Vitesse (Km sign)
The Km sign is used in conjunction with TIVs to indicate transition points of the speed limit when these do not coincide with notable landmarks.
Route Indicators
Routes are signaled with either an Indicateur de Direction (ID) or a Tableau Indicateur de Direction à Distance (TIDD), or both.
Indicateur de Direction
An Indicateur de Direction (ID) is typically grouped with the Carré signal preceding the relevant facing point(s).
- railway:signal:route=FR:ID
- railway:signal:route:form=light
- railway:signal:route:states=(FR:ID1/FR:ID2/FR:ID3/FR:ID4/FR:ID5)
Tableau Indicateur de Direction à Distance
The Tableau Indicateur de Direction à Distance (TIDD) indicates the position of the next point, either left or right unless the next signal displays a closed Carré in which case, the TIDD is off.
- railway:signal:route_distant=FR:TIDD
- railway:signal:route_distant:form=light
- railway:signal:route_distant:states=(off/left/right)
Embranchements
The BIF board announces a trailing switch junction with multiple tracks.
The Y board announces a facing switch junction.
Cab Signalling
Conventional Railway Lines
Cab signalling of type Contrôle de Vitesse par Balises (Speed control by beacons, KVB) or European Train Control System (ETCS).
The train is directed towards a cab signalling line. One or more boards of this type precede the entry.
- railway:signal:train_protection=FR:CAB_E
- railway:signal:train_protection:form=sign
- railway:signal:train_protection:type=distant
The train enters a cab signalling line. This sign is at the position of the last signal or immediately downstream of that signal.
- railway:signal:train_protection=FR:CAB_R
- railway:signal:train_protection:form=sign
- railway:signal:train_protection:function=entry
- railway:signal:train_protection:type=(FR:KVB/FR:ETSC)
The train is returning to a traditional lateral signalling line.
- railway:signal:train_protection=FR:CAB_S
- railway:signal:train_protection:form=sign
- railway:signal:train_protection:function=exit
Highspeed Railway Lines
Cab signalling of type Transmission Voie-Machine (TVM) or European Train Control System (ETCS).
Block Markers
- railway:signal:train_protection=FR:REP_TGV
- railway:signal:train_protection:form=sign
- railway:signal:train_protection:function=block
Shunting Markers
A shunting marker or Jalon de Manœuvre is placed at a point where certain train movements are executed. These movements may include reversing, shunting, or departing trains from a work site. The white chevron points to the track involved.
Wrong Ways
These signs are used on double-track sections equipped with wrong-way installations or Installations de contresens (ICS).
The Tableau d'Entrée de Contresens (TECS) indicates or confirms to the driver that the train is directed in the wrong way.
- railway:signal:wrong_route=FR:TECS
- railway:signal:wrong_route:form=sign
- railway:signal:wrong_route:function=entry
The Tableau de Sortie de Contresens (TSCS) indicates to the driver that the train, currently running in the wrong way, is now directed in the normal direction.
- railway:signal:wrong_route=FR:TSCS
- railway:signal:wrong_route:form=sign
- railway:signal:wrong_route:function=exit
Stations and Facilities
Announcements
This type of sign indicates the distance to the next facility.
- railway:signal:station_distant=FR:APPROCHE_ETS
- railway:signal:station_distant:form=sign
- railway:signal:station_distant:caption=* (e.g. "Chailles à 200m")
The Gare sign indicates the approach to a facility where special regulations for stations apply. Typically, a downward-pointing chevron placed in front of the entry point marks the entrance to the facility.
This sign marks the approach to a facility, other than a station, where points must not be passed at a speed exceeding 30 km/h (40 km/h on certain lines).
Note: the last couple of signs are specific to single tracks with simplified signalling, known as Voie Unique à Signalisation Simplifiée (VUSS).
Stops
- railway:signal:stop=FR:ARRET_A
- railway:signal:stop:form=sign
- railway:signal:stop:caption=* (optional, text written on the sign)
- railway:signal:station_distant=FR:STOP_A
- railway:signal:station_distant:form=sign
- railway:signal:station_distant:caption=* (optional, text written on the sign)
The Jalon d'Arrêt (Stop Marker) is similar to the Carré signal; it commands a stop before the point where it is placed and cannot be crossed.
Passenger Stops
Signs used in certain facilities to mark the stopping point for passenger trains.
Stopping point for the front of the train (Tête de Train), regardless of the number of vehicles in the train.
Stopping point for the front of the train (Tête de Train), regardless of the number of vehicles in the train, including the locomotive.
Stopping point for trains equipped for driver-only operations, referred to as Équipé Agent Seul (EAS).
Stopping point for trains composed of the number of carriages indicated on the sign.
- railway:signal:stop=FR:ARRET_V
- railway:signal:stop:form=sign
- railway:signal:stop:for=vehicles
- railway:signal:stop:caption=* (text written on the sign)
Stopping point for TGVs. The number indicates the number of rakes: 1=single unit, 2=multiple units.
- railway:signal:stop=FR:ARRET_TGV
- railway:signal:stop:form=sign
- railway:signal:stop:for=multiple_unit
- railway:signal:stop=FR:ARRET_TGV
- railway:signal:stop:form=sign
- railway:signal:stop:for=single_unit;multiple_unit
Train Departure
Departure Request
Some Carré signals are equipped with a Demande de Départ (DD) plate. The driver waiting for departure must, one minute before the scheduled departure time or if they notice the corresponding Carré signal has opened, request departure authorization by telephone.
Departure Authorization
At the exit of certain tracks, departure authorization may be given to the driver by means of a flashing half-white, half-green Signal Lumineux de Départ (SLD).
- railway:signal:departure=FR:SLD
- railway:signal:departure:form=light
- railway:signal:departure:states=(on/off)
Alternatively, departure authorization may be given simply by the opening of the corresponding Carré signal; these Carré signals are identified by a half-white, half-green plate.
Service Tracks and Shunting
Some yards or groups of converging tracks have dedicated exit signalling.
Upward-pointing Chevrons
Upward-pointing chevrons indicate either an exit from a junction of converging tracks or, in some stations, the point beyond which trains must not proceed when a stop is required.
Tableau Lumineux de Correspondance
A Tableau Lumineux de Correspondance (TLC) for converging tracks is a signal installed at ground level to the left of the track it addresses and is normally off. At any given time, it can display one of the following:
- A white letter T, either fixed if the group signal is open or flashing, if the group signal is closed.
- The Signal Lumineux de Départ if applicable.
- A red and white checkerboard, which has the same meaning as the Jalon d'Arrêt and is used instead of the Chevron.
- railway:signal:shunting=FR:TLC
- railway:signal:shunting:form=light
- railway:signal:shunting:states=(FR:T/FR:(T)/FR:SLD/FR:MARKER)
Tableau lumineux Indicateur de Provenance
At the exit of some service track yards, a Tableau lumineux Indicateur de Provenance (TIP), a track indicator, complements the chevron. It can display any of the numbers designating each of the tracks. When the TIP displays a number, the driver on the corresponding track is allowed to cross the chevron. When the group signal is closed, the driver can advance to an agreed point, usually in preparation for a reversing movement.
Signal Lumineux de Manœuvre
A Signal Lumineux de Manœuvre (SLM) is installed in some facilities to facilitate maneuvers involving the execution of shunting movements on the main track (such as the parking of a train by pushing) or on a service track. It consists of three white lights, which are normally off.
- railway:signal:shunting=FR:SLM
- railway:signal:shunting:form=light
- railway:signal:shunting:states=(FR:PUSH/FR:PULL/FR:STOP)
Electrified Railway Lines
Neutral Zones
A neutral zone (or zone de sectionnement) is a grounded catenary zone, isolated on both sides, used to separate portions of track either powered by different substations or phases, or when switching voltages from 1500V DC to 25kV AC and vice versa, or to accommodate different voltages and frequencies in cross-border areas.
The main circuit breaker must be opened while the train passes through this zone, which it traverses using its own kinetic energy (marche sur l'erre).
Neutral Zone Announcement
The distant signal announces a neutral zone at the specified distance in meters.
- railway:signal:electricity=FR:SECT
- railway:signal:electricity:form=sign
- railway:signal:electricity:type=power_off_advance
- railway:signal:electricity:distance=* (specified distance in meters)
Start of Neutral Zone
Execution signal.
- railway:signal:electricity=FR:CC_EXE
- railway:signal:electricity:form=sign
- railway:signal:electricity:type=power_off
- railway:signal:electricity:function=entry
End of Neutral Zone
Signals indicating the end of the neutral zone.
- railway:signal:electricity=FR:CC_FIN
- railway:signal:electricity:form=sign
- railway:signal:electricity:type=power_on
- railway:signal:electricity:function=exit
- railway:signal:electricity:voltage=* Voltage of the current line; usually 1500V or 25kV. (optional)
- railway:signal:electricity:frequency=* Frequency of the current on the current line; usually 50Hz for 25kV. (optional)
End of the neutral zone for reversible trains or trains with multiple pantographs.
- railway:signal:electricity=FR:REV
- railway:signal:electricity:form=sign
- railway:signal:electricity:function=exit
- railway:signal:electricity:type=power_on
- railway:signal:electricity:voltage=*
- railway:signal:electricity:frequency=*
Pantographs
Pantograph Down Announcement
Distant Pantograph Down signal (signal à distance "Baissez panto").
This signal instructs the lowering of the train's pantograph(s) under specific circumstances:
- Transition from 1500V DC to 25kV AC: Required when switching from direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) power supply.
- Between Two 25kV Substations: Necessary due to phase shift, which can cause a potential difference of up to 70kV at a 180° phase difference.
- Phase Change: Used to redistribute the electrical load within the network.
- Cross-border Areas: Needed when crossing borders where different electrical systems may be in operation.
- Crossing Certain Structures: Specific structures may require the pantograph to be lowered for safety or operational reasons.
- railway:signal:electricity=FR:BP_DIS
- railway:signal:electricity:form=sign
- railway:signal:electricity:type=pantograph_down_advance
Start of Pantograph Down
Pantograph Down execution signal (signal d'exécution "Baissez Panto").
- railway:signal:electricity=FR:BP_EXE
- railway:signal:electricity:form=sign
- railway:signal:electricity:function=entry
- railway:signal:electricity:type=pantograph_down
- railway:signal:electricity:voltage=* (optional)
End of Pantograph Down
Signal indicating the end of the route with Pantograph Down (signal de fin de parcours "Baissez Panto" ).
- railway:signal:electricity=FR:BP_FIN
- railway:signal:electricity:form=sign
- railway:signal:electricity:function=exit
- railway:signal:electricity:type=pantograph_up
- railway:signal:electricity:voltage=* (optional)
Dual-Mode Traffic
Distant signal announcing traffic towards a non-electrified line. This sign accompanies the Baissez Panto (Pantograph Down) distant and execution signals when they apply only to dual-mode traffic. In this case, they are not followed by an End of Pantograph Down signal.
- railway:signal:dual_mode=FR:BIMODE_A
- railway:signal:dual_mode:form=sign
- railway:signal:dual_mode:caption=* (optional; text written on the sign)
- railway:signal:dual_mode:function=entry
Distant signal announcing traffic coming from a non-electrified line for dual-mode trains only. This sign accompanies the End of Pantograph Down signal when it applies only to dual-mode traffic. It is not preceded by the Baissez Panto (Pantograph Down) distant and execution signals.
- railway:signal:dual_mode=FR:BIMODE
- railway:signal:dual_mode:form=sign
- railway:signal:dual_mode:function=exit
End of Catenaries
Beyond this sign, the line is no longer electrified and only thermal or dual-mode trains can continue.
- railway:signal:electricity=FR:FIN_CAT
- railway:signal:electricity:form=sign
- railway:signal:electricity:type=end_of_catenary
- railway:signal:position=overhead
Stop Markers
The Jalon d'arrêt à damier bleu et blanc (blue and white checkered Stop Marker), which only exists on service tracks, commands the stop of shunting movements of electric trains.
Frost Board
Level Crossings
Level crossing announcement.
- railway:signal:crossing_distant=FR:PN_A
- railway:signal:crossing_distant:form=sign
- railway:signal:crossing_distant:caption=* (optional; text written on the sign)
- railway:signal:crossing_info=FR:PN
- railway:signal:crossing_info:form=sign
- railway:signal:crossing_info:caption=* (optional; text written on the sign)
Whistle
The S board indicates the locations where the driver must sound the horn, for example, approaching unguarded level crossings, or at the entrance of tunnels, or in areas with reduced visibility.
When a J plate is present below the S sign, the obligation to whistle is only imposed on the driver during daytime (between 07:00 and 20:00).
- railway:signal:whistle=FR:SIFFLER
- railway:signal:whistle:form=sign
- railway:signal:whistle:plate=FR:J
Miscellaneous Signs and Boards
The G (Garage) board indicates that the train is directed towards a service track.
The D (Depot) board indicates that the train is directed towards depot tracks.
The LGR (Limite pour Garage par Refoulement) board.
LM (Limite de Manœuvre) board.
MV (Marche à Vue) board.
The IMP (Impasse) board indicates that the train is directed towards a dead-end track. .
The Heurtoir à xxx mètres board announces a buffer stop at the specified distance.
- railway:signal:shunting=FR:HEURTOIR_A
- railway:signal:shunting:form=sign
- railway:signal:shunting:type=buffer_stop
- railway:signal:shunting:distance=* (specified distance in meters)
The SAS board indicates that the train is directed towards a generally very short section of track (sas) with Carré signals at each end.
- railway:signal:shunting=FR:SAS
- railway:signal:shunting:form=sign
- railway:signal:shunting:short_route=yes
The diamond-shaped sign below marks the boundary of certain facilities.
Zone with reduced loading gauge.
Sources
- French railway signalling]
- Signalisation permanente (SNCF)
- Lexique des acronymes (SNCF)
- Signalisation au sol (SNCF, 2005, PDF)
- signalisation-rfn-svg (Nicolas Wurtz, SVG)
- Diagrams of railway signals in France (Various authors, SVG+GIF)